# 认识路由
# 后端路由
- 服务器直接生产渲染好对应的HTML页面,返回给客户端进行展示(jsp)
# 前后端分离阶段(随着ajax的出现)
- 后端只负责提供数据,不负责任何阶段的内容。浏览器中显示的网页中的大部分内容,都是由前端写的js代码在浏览器中执行,最终渲染出来的网页。
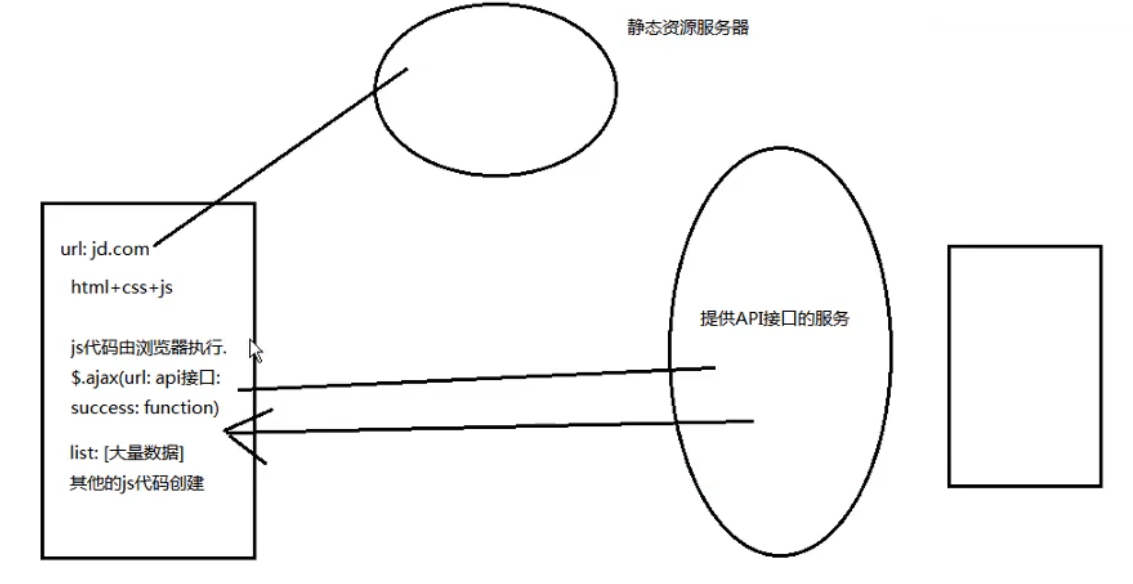
- 优点:前后端责任清晰,后端专注于数据上,前端专注于交互和可视化上。即使移动端出现后,后端不需要进行任何处理,依然可以使用之前的一套API即可。
# SPA(单页面富应用阶段)
- 第一步:发送url请求,获取全部的资源(CSS + HTML +js)
- 第二步:当发送新的url请求时,将通过前端路由,去全部资源中获得自己需要的组件,在前端页面进行展示
# 基本使用
# 避免URL刷新的两种方式
# hash
Location.hash ='aaa'(该字符串将会直接加载url的后面)
1
# history
//第一种
history.back()等价于的history.go(-1)
history.forward() 等价于 history.go(1)
//第二种
history.pushState({},'','/foo')相当于栈的方式,默认显示栈顶元素
history.back() 出栈
//第三种(相当于直接把url进行了替换,浏览器不会对其有缓存,所以不能返回上一步操作)
history.replaceState({},'','home')
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# vue-router的安装与配置
# 手动配置安装(框架)
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Vue from 'vue'
//第一步,安装路由插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes =[{path:'/home'},component:cpn]
//第二步,创建路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
//配置路由和组件之间的应用关系
routes,
mode:'history'//默认模式是hash模式
})
//第三步,将router的对象传入到Vue实例中
export default router
//使用vue-router的步骤
创建路由组件
配置路由映射:组件和路径映射关系
使用路由:通过<router-link>和<router-view>,router-link进行关系的映射,router-view是提供占位符,表示组件将要展示的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 路由的默认路径
//配置这些默认路由,path=''和'/'效果是等同的,另外对于这些有特殊的情况的路由,一般放在最前面(推荐使用)或者最后面
const router =[{
path:'/',
redirect:'/home'
}]
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# router-link属性的配置
属性:to 用于指定跳转的路径
tag:<router-link to='/home' tag='li'></router-link>默认渲染的a标签,可以通过tag属性可以改变渲染标签
replace:取消的浏览器对当前页面的缓存,不允许页面返回
active-class:当<router-link>对应的路由匹配成功时,会自定给当前元素设置一个router-link-active的class,设置active-class可以修改默认的名称:
在router实例中进行修改
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'active'
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 路由代码跳转
<template>
<button @click="linkToHome">
首页
</button>
<button @click="linkToAbout">
关于
</button>
</template>
export default{
name:'App',
methods:{
linkToHome(){
this.$router.push('/home')
},
linkToAbout(){
this.$router.push('/about')
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 动态路由
//通过绑定的方式去获取vue实例中的data数据,从未达到动态变化的效果
<router-link :to="'/home/'+userName" tag='li'></router-link>
//index.js(路由中的js文件)
routes: [
{
path: '/home/:useid',//:useid可以通过的this.$route.param.useid拿到
component: Home
}
]
//打包文件的解析(默认将我们的js文件打包到以下的js文件中)
含有app命名的js文件,当前应用程序开发的所有代码(业务代码)
含有manifest的js文件,为了打包的代码做底层支撑
含有vendor的js文件,主要是第三方的代码 vue/vue-router/axios/bs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 路由的懒加载
- 避免一次性的请求的js文件太多,造成用户的电脑出现了短暂的空白的情况。
- 解决方法:把不同的路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应的组件,这样就更加的高效
//路由的懒加载的代码(一个懒加载,对应一个js文件)
const routes =[
{
path:'/home',
component:()=>import('../components/Home')
},
{
path:'/about',
component:()=>import('../components/About')
}]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 路由的嵌套
const routes =[
{
path:'/home',
component:()=>import('../components/Home'),
children:[
{
path:'news',
component:()=>import('../components/News')
},
{
path:'/message',
component:()=>import('../components/Message')
}
]
},
{
path:'/about',
component:()=>import('../components/About')
}]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 参数的传递(params 和 query)
params的类型:
配置的路由的格式:/router/:id
传递的方式:在path后面跟上对应的值
传递之后形成的路径:/router/123,/router/abc
query的类型:
配置路由格式:/router,也就是普通配置
传递的方式:对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
传递后形成的路径:/router?id=123,/router?id=abc
URL:scheme://host:port/path?query#fragment
通过代码的方式进行参数的传递
<template>
<button @click="linkToHome">
首页
</button>
<button @click="linkToAbout">
关于
</button>
</template>
export default{
name:'App',
methods:{
linkToHome(){
this.$router.push({
path:'/home',
query:{name:'kobe',age:19,height:1.87}
})
},
linkToAbout(){
this.$router.push('/about')
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
所有的组件均继承Vue.prototype
响应式实现的核心:object.defineProperty(obj,'age',18)
1
2
2
# 导航守卫
- 当页面发生跳转的过程中,我们对该过程进行监听,当发生之后执行我们得想要执行得事件
- 除了全局的导航守卫,还包路由独享守卫和组件内的守卫
//虽然下面的代码能够实现我们想要的效果,但是如果组件太多的话,每个都要加,将会变得十分麻烦
export default {
name:"Home",
data(){
return{
message:'我的世界将是星辰大海'
}
},
created(){//组件在创建出来的时候进行执行
console.log('created');
},
mounted(){//组件挂载到vue实例的时候进行执行
console.log('mounted');
},
updated(){//组件发生更新的时候进行执行
console.log('updated');
}
}
//全局导航守卫的第二种实现方式
//第一步:为各个组件设置meta属性 ???
//第二步:在index.js中配置前置钩子(hook)
//注释:to 将要访问的路径 from 代表从那个路径跳转而来 next 是一个函数,表示放行 next()放行 next('/login') 强制跳转
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
//从from跳转到to
document.title = to.matched[0].meta.title
console.log(to)
next()
})
//后置勾子,也就是afterEach,不需要主动调用next()函数
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- 利用导航首位设置登录页面的路由跳转
//第一步:及那个导航首位挂载到路由上
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
//如果访问的首页,则直接进行放行
if('/login'=== to.path) next();
//如果访问的不是首页地址,则获取token进行判断,如果含有token则直接进行放行,如果没有token则进行强制跳转
const tokenStr = window.sessionStorage.getItem('token')
if(!tokenStr){
next('/login');
}
next();
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# keep-alive
- 当跳转结束之后,再次跳转的时候仍然是之前的页面展示的效果
//第一步 keep-alive标签
<keep-alive>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
只用当使用了keep-alive的时候,activated和deactivated这两个函数才是有效的
//利用组件内的导航
export default {
name:"Home",
data(){
return{
message:'我的世界将是星辰大海'
}
},
created(){//组件在创建出来的时候进行执行
console.log('created');
},
mounted(){//组件挂载到vue实例的时候进行执行
console.log('mounted');
},
updated(){//组件发生更新的时候进行执行
console.log('updated');
},
//替换默认的路由
activated(){
this.$router.push(this.path)
}
//利用组件内的导航守卫
beforeRouteLeave(to,from,next){
console.log(this.$route.path)
this.path = this.$route.path;
next();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
- keep-alive的相关属性
exclude="Profile,User"(逗号之后不要随意加空格,该属性代表除了这些组件以外,其他的元素只创建一次)
include="字符串或者正则表达式"
1
2
2
注意:所有的正则表达式不要随意的添加空格
注意:在vue组件中的样式中想要引入外部的样式文件,需要用以下的特殊的方式
@import "./assets/css/base.css"
1
